Ultracold atom systems placed in an optical resonator provide versatile theoretical and experimental platforms for studying many-body quantum physics, entanglement, quantum simulation and computation, quantum measurement, and a variety of other topics. However, the ubiquitous decoherence will hinder the achievable phase sensitivity especially in the long evolution time required for cyclic dynamics.
We propose a cavity-aided nonlinear atom interferometer, based on the quasi-periodic spin mixing dynamics of an atomic spin-1 Bose–Einstein condensate trapped in an optical cavity, in which cavity-mediated nonlinear interactions give rise to saddle points in the semiclassical phase space, providing a general mechanism for exponential fast scrambling and metrological gain augment. We unravel that the phase sensitivity can be greatly enhanced with the cavity-mediated nonlinear interaction. The research is useful to understand the intrinsic relation between the concepts from different subfields of quantum science.
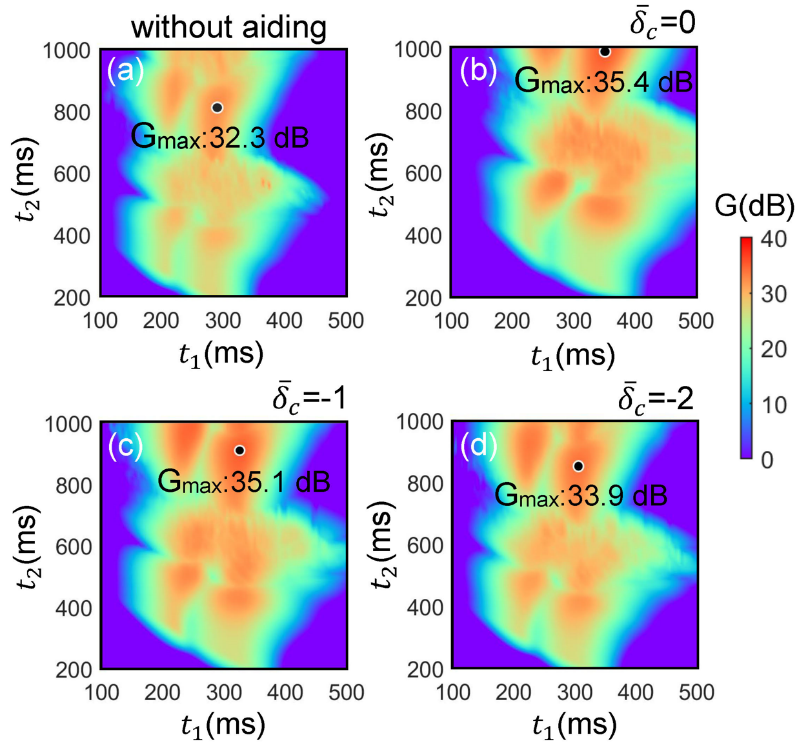
Fig.1: (a) Quasi-periodic spin mixing dynamics in a spin-1 atomic nonlinear interferometer. (b) A nonlinear interferometer implemented with a spin-1 atomic condensate trapped in a unidirectional ring cavity.
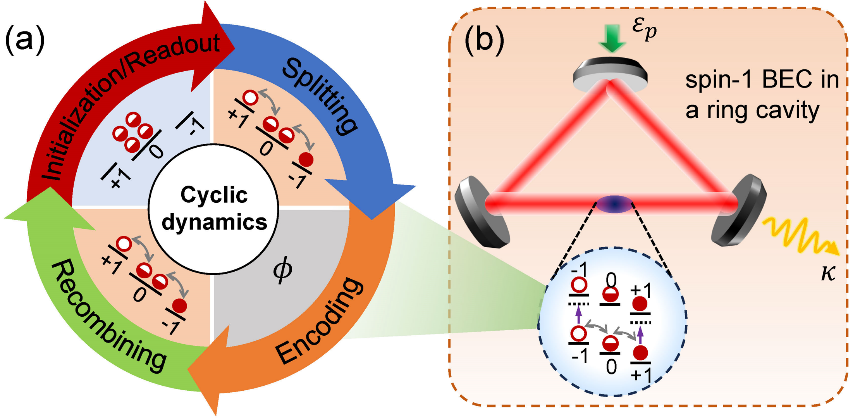
Fig.2:The optimal metrological gain over relative phase rad as a function of splitting and combining time.
The corresponding research papers, titled "Cavity-enhanced metrology in an atomic spin-1 Bose-Einstein condensate" and "Improving metrology with quantum scrambling in a spin-1 Bose-Einstein condensate coupled to a cavity" were published on the journal "Frontiers of Physics" (19,32204 (2024)) and "Optics Express" (32,25207 (2024))
The first affiliated institution for the research is Hefei University of Technology. The first author is Doctor Renfei Zheng from Department of Physics, and the corresponding author is Associate Professor Lu Zhou from East China Normal University. Other co-authors are Professor Bing Chen and Doctor Zhifei Yu. The research received support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and other funding sources.
Link to the original research papers: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-023-1372-5
https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.527465